
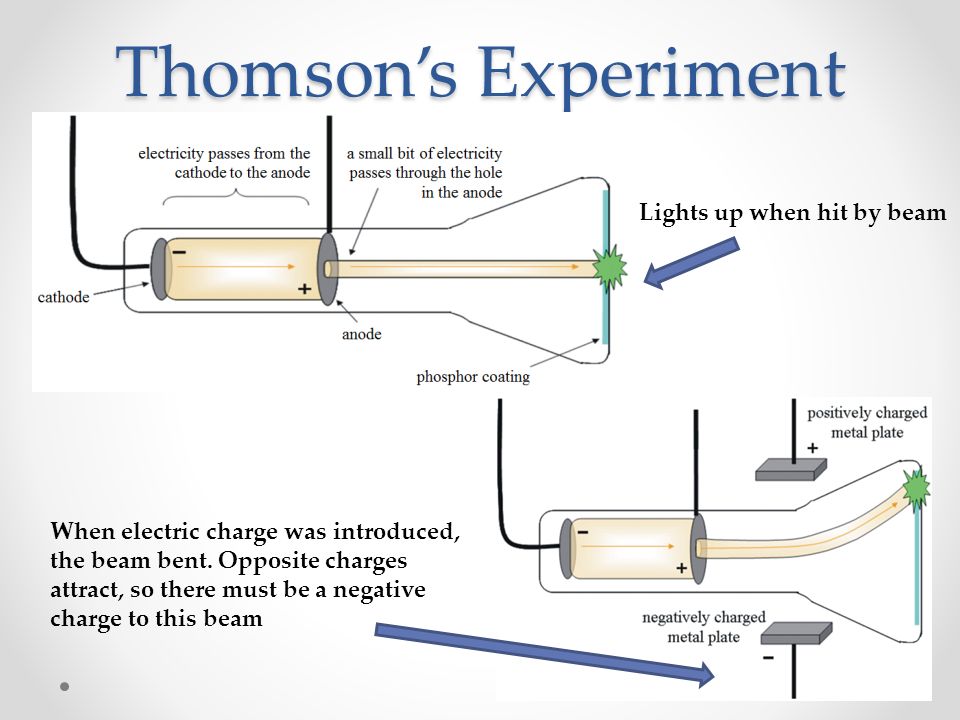
However, the positively charged part of an atom was not yet well understood. Scientists had now established that the atom was not indivisible as Dalton had believed, and due to the work of Thomson, Millikan, and others, the charge and mass of the negative, subatomic particles-the electrons-were known. Thomson had many famous students, including Ernest Rutherford.\( \newcommand \] He did this using a cathode ray tube, which is a vacuum-sealed tube with a cathode and anode on one end that create a beam of electrons travelling towards the other end of the tube. Strangely, another author with the name JJ Thomson wrote a book with the same name in 1975. Thomson discovered the existence of electrons. He died in 1940, buried near Isaac Newton and Charles Darwin. A year earlier, in 1936, Thomson wrote an autobiography called “Recollections and Reflections”. Not only did Thomson receive the Nobel Prize in physics in 1906, but his son Sir George Paget Thomson won the prize in 1937. Thomson’s work provided the foundation for the work done by many other important scientists such as Einstein, Schrodinger, and Feynman. In turn chemical bonds are essential to the reactions taking place around us every day. We now know the electron forms the basis of all chemical bonds. Although Thomson didn’t know it, the electron would turn out to be one of the most important particles in chemistry. The discovery of the electron was the first step in a long journey towards a better understanding of the atom and chemical bonding. Why was the discovery of the electron important? The name electron was suggested by George Francis Fitzgerald. Thomson called the particle “corpuscles”, not an electron. Thomson finally proved atoms were made up of smaller components, something scientists had been puzzled by for a long time. Thomson was now able to determine that the particles in question were much smaller than atoms, but still highly charged. These were the two critical pieces of information that lead to the discovery of the electron. Using this information Thomson determined the mass to charge ratio of an electron. Then Thomson measured how much various strengths of magnetic fields bent the particles. Thomson was able to deflect the cathode ray towards a positively charged plate deduce that the particles in the beam were negatively charged. Thomson also determined the mass to charge ratio of the electron using a cathode ray tube, another significant discovery. Cathode rays are formed when electrons emitted from one electrode and travel to another when a voltage is applied in a vacuum. Thomson determined that charged particles much lighter than atoms, particles that we now call electrons made up cathode rays.

Cathode rays played a critical role in unlocking this mystery. Yet until Thomson, no one had determined what these might be.
Prior to the discovery of the electron, several scientists had posited that atoms might be made up of smaller pieces.

In his second experiment he wanted to see if the rays would bend in the presence of an electrical field, which is what you would expect for a charged particle. He found that the rays were bent and the negative charge was bent exactly the same. What is a cathode ray tube and why was it important? Thomson set up his cathode ray tube with, but placed a magnet above the path of the rays. For instance, the discovery of the electron was vital to the development of chemistry today, and it was the first subatomic particle to be discovered. Although he was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics and not chemistry, Thomson’s contributions to the field of chemistry are numerous. Thomson did most of this work while leading the famed Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge. In addition to this work, Thomson also performed the first-ever mass spectrometry experiments, discovered the first isotope and made important contributions both to the understanding of positively charged particles and electrical conductivity in gases. After much experimentation, Thomson confirmed that the cathode rays were always deflected by a negatively charged plate at the end of the tube. Thompson made the switch to physics a few years later and began studying the properties of cathode rays. Thompson was born in December 1856 in Manchester, England and was educated at the University of Manchester and then the University of Cambridge, graduating with a degree in mathematics.
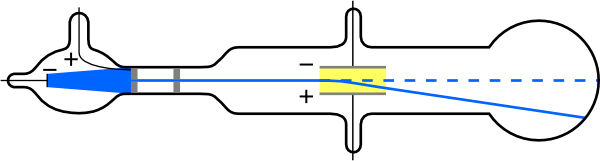
JJ Thomson was an English physicist who discovered the electron in 1897.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
